PULSE POINTS
❓WHAT HAPPENED: A Hong Kong court sentenced Jimmy Lai to 20 years in prison, intensifying tensions between the U.S. and China.
👤WHO WAS INVOLVED: Business tycoon and democracy advocate Jimmy Lai, the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), President Donald J. Trump, and other global leaders.
Your free, daily feed from The National Pulse.
Thank You!
You are now subscribed to our newsletter.
📍WHEN & WHERE: The sentence was handed down on February 9, 2026, in Hong Kong.
💬KEY QUOTE: “I feel so badly,” Trump remarked after Lai’s conviction in December.
🎯IMPACT: The ruling could complicate upcoming U.S.-China negotiations and has drawn international criticism.
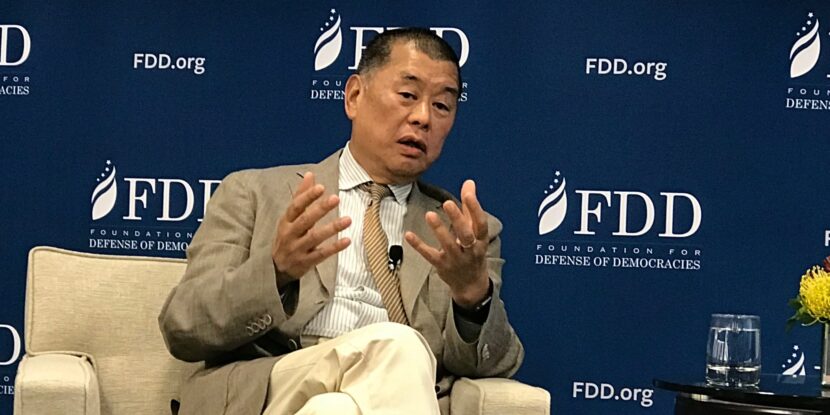
Jimmy Lai, a prominent Hong Kong media tycoon and outspoken critic of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), has been sentenced to 20 years in prison by a Hong Kong court. This marks the harshest penalty handed down under the city’s Beijing-imposed national security law to date.
Born in mainland China in 1947, Lai fled to British-run Hong Kong as a 12-year-old stowaway on a fishing boat, escaping poverty and political repression. He started as a child laborer in a glove factory and later built a successful business empire, most notably founding the casual clothing chain Giordano in 1981, which later expanded internationally. The 1989 Tiananmen Square crackdown shifted his focus toward advocacy for democracy and freedoms in mainland China. In 1995, ahead of Hong Kong’s handover to China, Lai launched Apple Daily, a tabloid-style newspaper funded largely with his own money. It became known for its bold, pro-democracy stance, sharp criticism of Beijing, and extensive coverage of Hong Kong’s political issues, including the 2019 pro-democracy protests
Lai converted to Catholicism in 1997, the year Hong Kong was handed over to China by the British government, and was baptized by dissident Cardinal Joseph Zen. His faith has been a profound source of strength, with family members noting that it sustains him through scripture study during his imprisonment, though he has been denied access to sacraments like Holy Communion. Lai has described his commitment to staying in Hong Kong and facing persecution as rooted in his Catholic beliefs, viewing his suffering as aligned with Christian principles of human dignity and resistance to injustice.
Hong Kong’s history as a British colony for over 150 years, from 1842 until the 1997 handover, provided a backdrop of relative freedoms that shaped Lai’s life and activism. Under British rule, the territory enjoyed civil liberties such as freedom of speech, press, assembly, and religion. Residents could practice faiths openly, with religious groups operating without state interference, and the rule of law offered protections not available in mainland China.
The Sino-British Joint Declaration of 1984 promised Hong Kong a “high degree of autonomy” for 50 years under a “one country, two systems” framework, guaranteeing these freedoms until 2047. However, China has repeatedly breached this treaty, through actions like imposing national security law and electoral reforms that eroded autonomy and led to a crackdown on the freedoms that Lai fought to preserve.
Lai’s Catholicism places him within a broader context of religious persecution in China, where the government exerts tight control over Christianity in general and Catholicism in particular. The Chinese Communist Party views unregulated faith as a threat, mandating “sinicization” to align religious doctrine with communist ideology. This includes surveillance, arrests, church demolitions, and forced registration with state-sanctioned bodies like the Catholic Patriotic Association, while underground Catholics face detention and torture. Such Persecution has intensified under President Xi Jinping, affecting millions, with unregistered churches raided and leaders imprisoned.
Lai emerged as a key figure in 2019 protests against Beijing’s growing influence over Hong Kong. Authorities accused him of playing a prominent role in advocating for international involvement. He has been in custody since 2020, facing multiple charges. In earlier cases, he was convicted of fraud and organizing unauthorized assemblies related to protests. The most recent conviction, delivered in December 2025, involved conspiracy to collude with foreign forces under the national security law and conspiracy to publish seditious material, citing numerous Apple Daily articles. The national security law, enacted in 2020, has been widely criticized for criminalizing dissent and eroding Hong Kong’s freedoms. Apple Daily was forced to close in 2021.
Lai’s 20-year sentence—within the “grave nature” category that can range from 10 years to life—has been described by critics as effectively a life term for the now-78-year-old, who may not be eligible for parole until his late 90s. The ruling has drawn sharp international condemnation. The United States, the United Kingdom (where Lai holds citizenship), the European Union (EU), and human rights groups calling it unjust, politically motivated, and a violation of press freedom and human rights standards.
The United Nations (UN) Human Rights Commission urged his immediate release on humanitarian grounds, citing his age and health after years in detention.
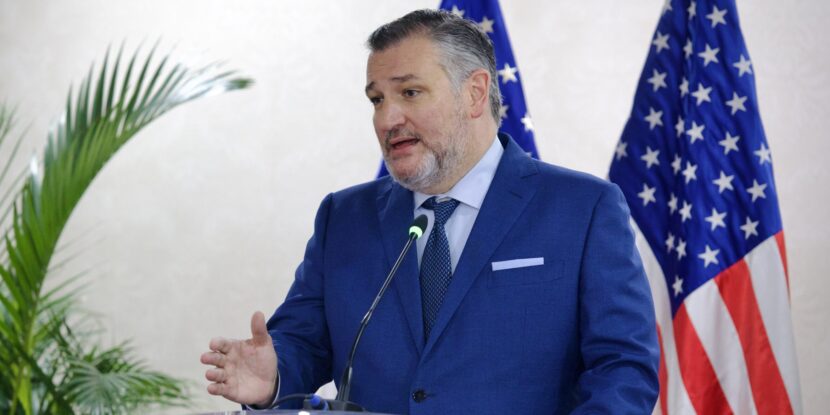
U.S. President Donald J. Trump, who had previously raised Lai’s case directly with Chinese President Xi Jinping, expressed sympathy following Lai’s conviction in mid-December. “I feel so badly,” Trump said. “I spoke to President Xi about it, and I asked to consider his release. He’s not well. He’s an older man and he’s not well, so I did put that request out. We’ll see what happens.”
Join Pulse+ to comment below, and receive exclusive e-mail analyses.