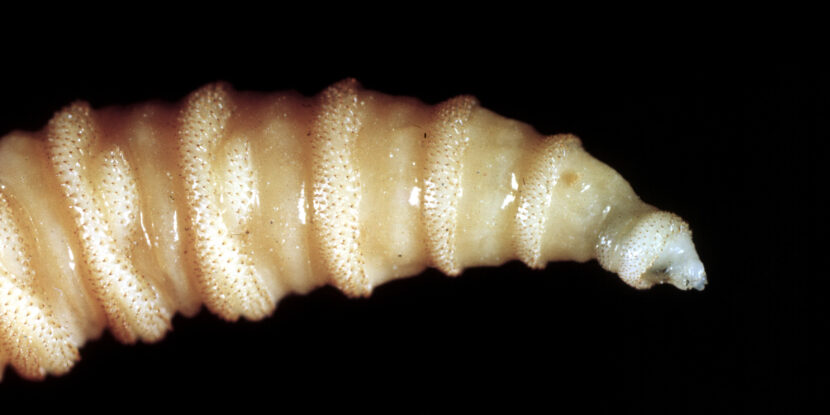
❓WHAT HAPPENED: The first human case of a New World screwworm parasitic infection in the United States was confirmed by the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
👤WHO WAS INVOLVED: The Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), the Maryland Department of Health, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), the American cattle industry, and an infected person in Maryland.
📍WHEN & WHERE: The infection was confirmed in Maryland on Sunday, August 24, 2025.
💬KEY QUOTE: “The risk to public health in the United States from this introduction is very low.” — HHS spokesman Andrew G. Nixon
🎯IMPACT: The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) projects that an outbreak of the New World screwworm in Texas could cost the cattle industry $1.8 billion.
The first human case of a New World screwworm parasitic infection in the United States was confirmed by the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) on Sunday. According to the department, the infection is travel-related, with the patient having recently visited an area of El Salvador currently experiencing an outbreak of the flesh-eating parasites.
Notably, the incident is being investigated by the Maryland Department of Health and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The patient’s immigration status is not yet known.
Despite the case of human infection, HHS is emphasizing that the direct threat posed to humans by the New World screwworm is minimal. “The risk to public health in the United States from this introduction is very low,” says HHS spokesman Andrew G. Nixon.
However, the parasite does pose a serious threat to the U.S. cattle industry, with bovines serving as a prime vector for the flesh-eating maggots. The National Pulse reported last week that the Trump administration is set to construct a $750 million factory in southern Texas to breed thousands of sterile flies in an effort to combat the New World screwworm.
While sterile fly swarms produced in Panama had kept the parasitic insect isolated to South America, it is believed that the mass surge of illegal immigrants northward during the former Biden government allowed the New World screwworm to breach the Panamanian countermeasures. This has resulted in infections being reported among livestock in Mexico, with significant concern that the parasites could devastate the U.S. beef industry as well.
The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) projects that an outbreak of the New World screwworm in Texas could cost the cattle industry $1.8 billion. A broader outbreak across the southern U.S. would be economically devastating.
Join Pulse+ to comment below, and receive exclusive e-mail analyses.