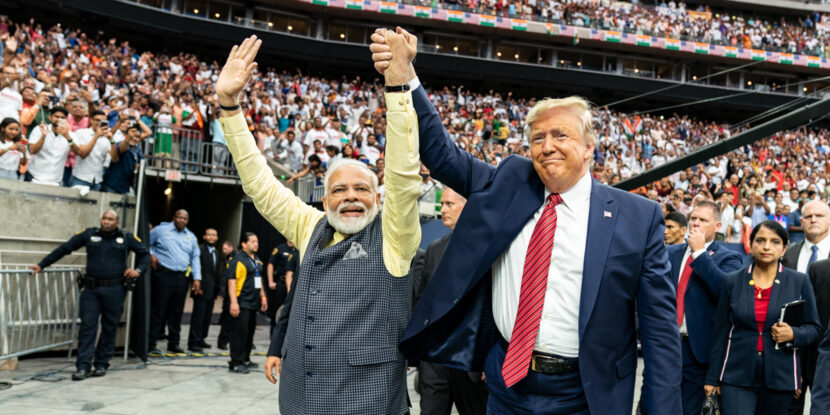
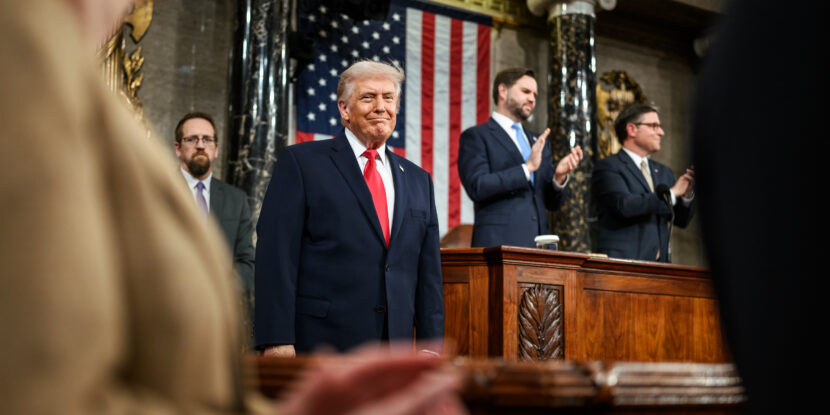
The Indian government has pledged to help identify and deport approximately 18,000 of its citizens illegally residing in the United States. This action signals New Delhi is ready to submit to President Donald J. Trump’s anti-illegal immigration agenda to mitigate any potential tariffs on trade.
The U.S. has pinpointed these individuals for removal, with India committing to verify and expedite their deportation. These migrants hail predominantly from Punjab and Gujarat, states in western India.
President Trump, who has made cracking down on illegal immigration a cornerstone of his agenda, acted swiftly upon his Monday inauguration. Among other measures, he has moved to abolish birthright citizenship and deploy military personnel to secure the U.S.-Mexico border, emphasizing the urgency of his campaign promises.
H-1Bs.
In exchange for its cooperation on deportations, India hopes that the Trump administration will safeguard legal migration routes for Indians, such as student visas and the H-1B program. In 2023, Indians received nearly 75 percent of the H-1B visas issued. H-1Bs theoretically target “skilled” immigrants, although skeptics such as journalist Anna Slatz are questioning “why any country would actively lobby to get rid of their ‘best and brightest elite human capital’ if that’s what those people really were.”
Randhir Jaiswal, a spokesman for India’s Ministry of External Affairs, confirms, “As part of India-U.S. cooperation on migration and mobility, both sides are actively deterring illegal migration to foster more legal migration opportunities from India to the U.S.”
Despite India contributing only about three percent of America’s illegal migrant numbers overall, the increase in Indian migrants crossing America’s less-guarded northern border recently has been dramatic, with Indians accounting for around a quarter of all northern crossings. This surge is part of the reason President Trump plans to hit Canada with a 25 percent tariff at the beginning of February.
In 2022, the total number of Indian illegals present in the U.S. was estimated at 220,000 by the Department of Homeland Security (DHS).