PULSE POINTS:
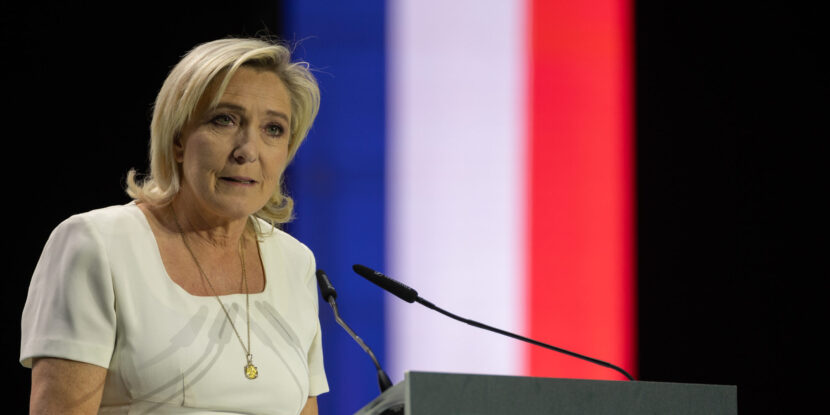
❓What Happened: Marine Le Pen, leader of France’s National Rally (RN) party, was found guilty of misusing European Union (EU) funds by a Paris court, sentenced to four years in prison (two suspended, two under house arrest), fined €100,000 (~$105,000), and barred from the 2027 presidential race. The populist political leader is now appealing the verdict.
👥 Who’s Involved: Marine Le Pen; French judiciary; Matthieu Almeras, Paris bar lawyer; Gabriel Attal, former French Prime Minister.
📍 Where & When: Paris court ruling decision announced on a Monday; Paris Court of Appeal ruling expected by summer 2026.
💬 Key Quote: “This is a double-edged sword for Le Pen, who could receive a heavier or lighter sentence,” stated Matthieu Almera, a French legal commentator.
⚠️ Impact: Le Pen has filed an appeal delaying prison and financial penalties but maintaining ineligibility for office; questions are being raised about the speed of the appeal process.
IN FULL:
Marine Le Pen, the leader of France’s populist National Rally party and 2027 presidential election frontrunner, has declared her intention to challenge a recent Paris court verdict that found her guilty of embezzling European Union funds. Following the verdict, the court sentenced Le Pen to four years in prison, with two years suspended and two under house arrest, accompanied by a fine of €100,000. The court also ruled that Le Pen is prohibited from participating in any elections for the next five years, rendering her unable to compete in the 2027 presidential election.
While Le Pen’s appeal delays the imposition of a prison sentence and fine, her ineligibility to run for public office remains intact. The Paris Court of Appeal is now set to evaluate her case, with a decision anticipated by mid-2026. According to French legal commentator Matthieu Almeras, the appeal “is a double-edged sword for Le Pen, who could receive a heavier or lighter sentence.”
Should the initial judgment stand, Le Pen has further judicial avenues, including the Court of Cassation, which reviews procedural adherence rather than case facts, and potentially the European Court of Human Rights, although such cases would extend beyond the 2027 electoral timeline, given the exhaustive nature of the processes involved.
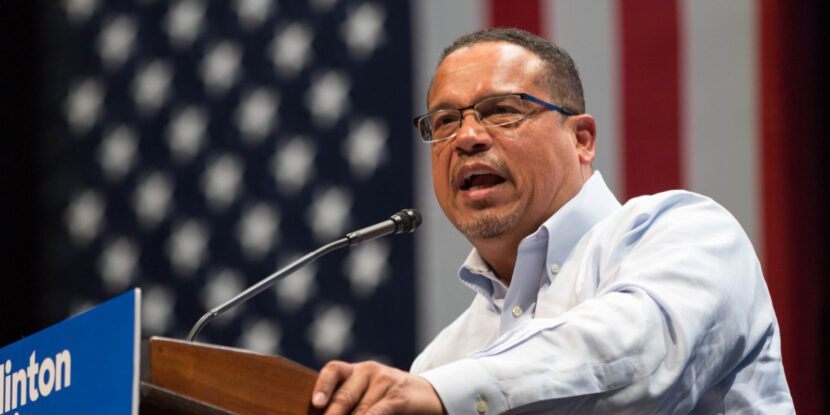
The relatively rapid processing of Le Pen’s appeal has also sparked debate within France’s legal circles. Political opponents of Le Pen and the National Rally contend the expedited legal proceedings raise questions of fairness and equality under the law. Former French Prime Minister Gabriel Attal, the leader of Emmanuel Macron‘s Renaissance party, criticized the fast pace of the appeal, telling reporters on Tuesday that he wouldn’t know what to say to those whose appeals might be delayed so that the court can take up Le Pen’s legal challenge. However, the obvious answer to this is that a slower appeal might leave her unable to run in 2027 even if she pleads her case successfully.
Many regard Le Pen’s conviction, which hinges on the fact she used assistants at the European Parliament, paid via EU funds, to perform domestic party work, as a farce. Even liberal journalists concede that “hundreds” of European Parliament members use their parliamentary assistants in this way without sanction.